What is AI-SPM? The New Category Securing Agentic AI
AI-SPM is the emerging security category for agentic AI. Learn what it means, why it matters, and how it differs from CSPM, DSPM, and traditional AppSec.
Every few years, a new security category emerges because the old ones can't keep up with how technology evolves.
CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) emerged because traditional network security couldn't handle dynamic cloud infrastructure. DSPM (Data Security Posture Management) emerged because data was moving faster than policies could track. And now, AI-SPM (AI Security Posture Management) is emerging because neither CSPM, DSPM, nor AppSec were built for autonomous AI agents.
But what exactly is AI-SPM? Is it just another vendor buzzword, or does it represent something fundamentally new?
We believe AI-SPM is a legitimate category—one that addresses gaps no existing security product was designed to fill. In this article, we'll break down what AI-SPM means, why it's necessary, and how it differs from the security tools you already have.
The Problem AI-SPM Solves
Before we define AI-SPM, let's understand the problem.
Here's a scenario that's playing out in enterprises everywhere: A product team deploys a customer support agent using Copilot Studio. A marketing team builds a content agent using LangChain. An engineering team experiments with autonomous coding agents. And IT? IT has no idea any of this is happening.
A majority of enterprises have deployed AI applications without full security visibility. Industry surveys consistently show that AI projects are being deployed faster than security teams can assess them—many organizations report their security review processes simply can't keep pace with AI adoption. That's the reality of how quickly AI is outpacing security governance.
Now, you might think: "We have CSPM for cloud risks. We have DSPM for data risks. We have SAST/DAST for application risks. Can't these tools handle AI too?"
The short answer: No. Here's why:
| Existing Category | What It Sees | What It Misses About AI |
|---|---|---|
| CSPM | Infrastructure misconfigurations | Agent behavior, reasoning, tool calls |
| DSPM | Data flows and classifications | AI-specific data patterns, RAG poisoning |
| AppSec (SAST/DAST) | Code vulnerabilities | Non-deterministic behavior, prompt injection |
| SIEM/SOAR | Logs and alerts | Semantic understanding of agent actions |
| IAM | User access | Agent identity, dynamic permissions |
Each of these categories was built for a world where applications behave predictably. AI agents break that assumption.
Defining AI-SPM
AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM) is the practice of continuously discovering, assessing, governing, and protecting AI systems across an organization—with a specific focus on the unique risks introduced by autonomous AI agents.
Let me break that down:
The Four Pillars of AI-SPM
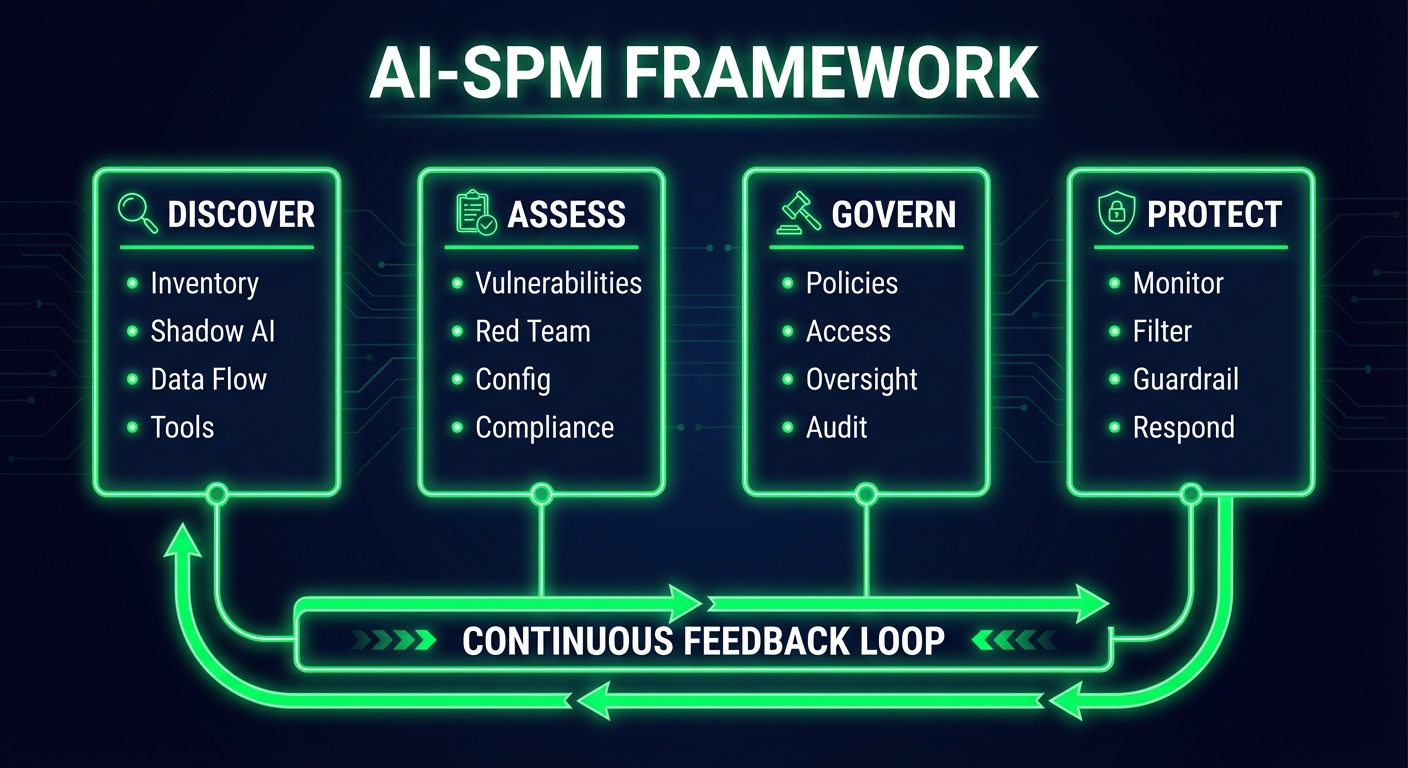
1. Discovery
You can't secure what you can't see. AI-SPM starts with discovering all AI systems in your environment:
- Authorized agents: Deployed through official channels
- Shadow AI: Unofficial deployments by teams and individuals
- Embedded AI: AI features within SaaS applications you use
- Third-party agents: AI systems from vendors and partners
Discovery isn't a one-time activity. New agents appear constantly as teams experiment and deploy. AI-SPM provides continuous visibility.
2. Assessment
Once you know what agents exist, you need to understand their risk:
- Vulnerability assessment: Prompt injection, tool abuse, memory attacks
- Configuration review: Are agents following security best practices?
- Privilege analysis: Do agents have more access than needed?
- Compliance mapping: How do agents align with regulatory requirements?
AI-SPM assessment goes beyond static scanning. Because agents are non-deterministic, you need dynamic testing that exercises their reasoning and behavior.
3. Governance
Governance establishes the rules for AI systems in your organization:
- Policies: What agents are allowed? What actions require approval?
- Access controls: Who can deploy, modify, or interact with agents?
- Human oversight: Which decisions require human confirmation?
- Accountability: Who is responsible when an agent acts?
AI governance is especially important given regulatory requirements like EU AI Act Article 14 (human oversight) and Article 13 (transparency).
4. Protection
Finally, AI-SPM includes runtime protection:
- Behavioral monitoring: Detect anomalous agent activity
- Input filtering: Block prompt injection and malicious content
- Output validation: Prevent sensitive data leakage
- Guardrails: Enforce boundaries on agent actions
Protection for AI must be semantic, not just syntactic. You're not just matching patterns—you're understanding intent. For example, a regex-based filter might block the word "delete," but an agent could be tricked into the same destructive action via "remove all records," "clear the table," or "reset to factory defaults." Semantic protection understands the intent of "transfer $10,000 to external account" is dangerous regardless of how it's phrased.
AI-SPM vs. Everything Else
Let's get specific about how AI-SPM differs from related security categories.
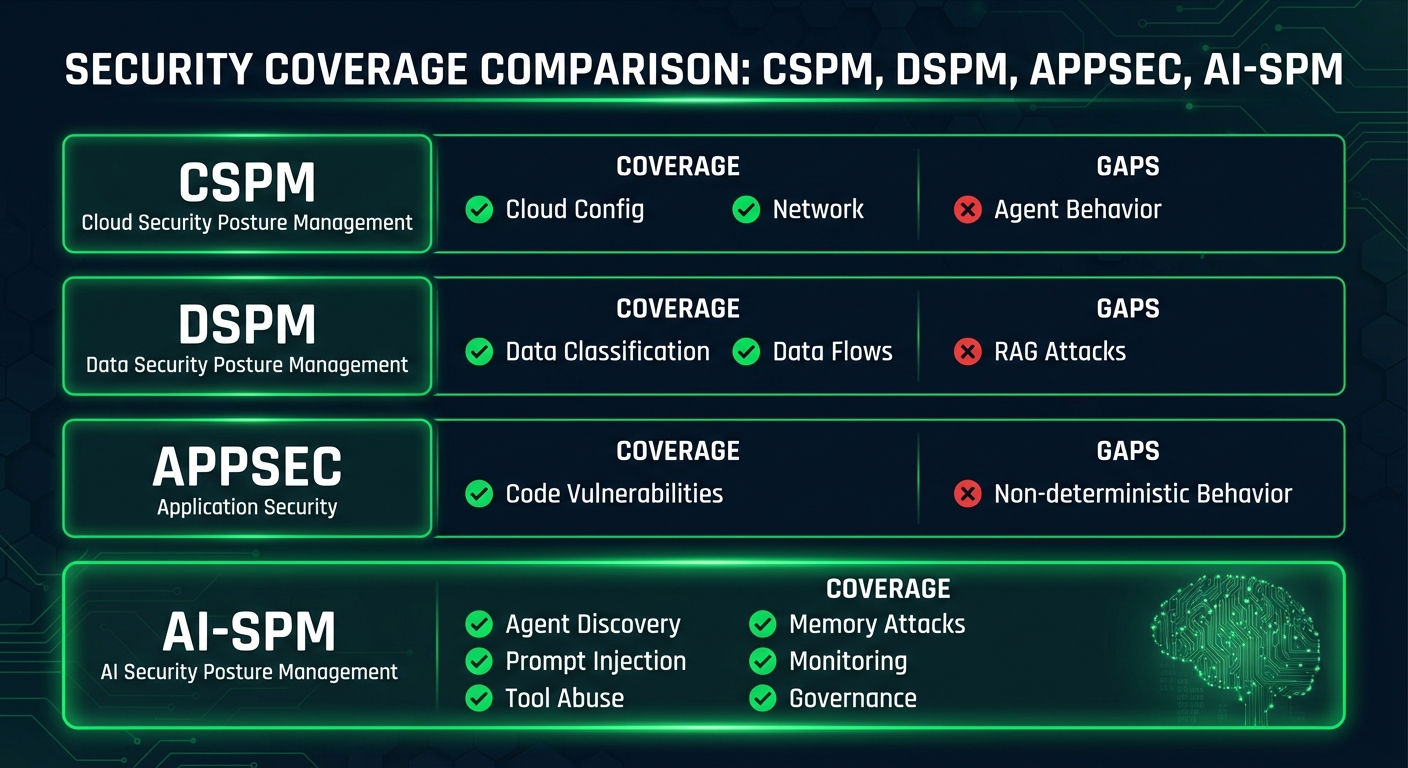
AI-SPM vs. CSPM
Cloud Security Posture Management focuses on infrastructure:
- Are S3 buckets public?
- Are security groups properly configured?
- Is encryption enabled?
CSPM sees the infrastructure that AI runs on, but it doesn't see the AI itself. CSPM can't tell you:
- What your agents are doing
- What data they're accessing
- Whether they're vulnerable to prompt injection
- If they're following your policies
AI-SPM complements CSPM by providing visibility into the AI layer that runs on your cloud infrastructure.
AI-SPM vs. DSPM
Data Security Posture Management focuses on data:
- Where is sensitive data stored?
- Who has access to it?
- Is it properly classified?
DSPM is valuable for AI security—after all, AI agents often access sensitive data. But DSPM misses:
- AI-specific data flows (prompts, responses, tool calls)
- RAG knowledge base risks
- Agent memory as a data store
- Data exfiltration through agent conversations
AI-SPM extends DSPM to understand how AI specifically interacts with data.
AI-SPM vs. AppSec
Application Security (SAST, DAST, SCA) focuses on code:
- Are there SQL injection vulnerabilities?
- Are dependencies up to date?
- Does the code follow secure patterns?
AppSec was built for deterministic applications. It struggles with AI because:
- You can't SAST an agent's "reasoning"
- DAST assumes predictable input/output mappings
- Prompt injection isn't in traditional vulnerability databases
AI-SPM provides AppSec for the AI era—vulnerability assessment designed for non-deterministic systems.
AI-SPM vs. MLSecOps
MLSecOps focuses on the machine learning lifecycle:
- Model training security
- Data pipeline protection
- Model versioning and integrity
MLSecOps is important but typically focuses on the development of models. AI-SPM focuses on the deployment and operation of agents that use those models. They're complementary—MLSecOps secures how models are built; AI-SPM secures how agents are run.
The AI-SPM Capability Stack
What does an AI-SPM solution actually do? Here's the capability stack:
Discovery Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Agent Inventory | Maintain a complete registry of all AI agents |
| Shadow AI Detection | Find unauthorized AI deployments |
| Platform Coverage | Discover agents across Copilot, AgentForce, LangChain, etc. |
| Data Flow Mapping | Understand what data each agent accesses |
| Tool/MCP Mapping | Document all tools and APIs agents can call |
Assessment Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability Scanning | Detect prompt injection, tool abuse, memory attacks |
| Red Teaming | Actively test agent security through adversarial techniques |
| Configuration Audit | Check agents against security benchmarks |
| Privilege Analysis | Identify excessive permissions |
| Compliance Mapping | Map agents to EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, ISO 42001 |
Governance Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Policy Management | Define and enforce agent security policies |
| Access Control | Manage who can interact with agents |
| Human Oversight | Enforce approval workflows for sensitive actions |
| Audit Logging | Complete trail of agent activities |
| Evidence Collection | Gather proof for compliance audits |
Protection Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Prompt Filtering | Block malicious inputs |
| Behavioral Monitoring | Detect anomalous agent behavior |
| Output Filtering | Prevent sensitive data in responses |
| Guardrails | Enforce boundaries on agent actions |
| Incident Response | Contain and investigate agent compromises |
Who Needs AI-SPM?
AI-SPM isn't for everyone—at least not yet. But if any of these describe your organization, you should be thinking about it:
You're Deploying Enterprise Agents
If you're using:
- Microsoft Copilot Studio
- Salesforce AgentForce
- ServiceNow AI Agents
- AWS Bedrock Agents
- Google Vertex AI Agents
- Any custom agents on LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen
...then you need AI-SPM. These platforms enable powerful capabilities, but the security responsibility falls on you.
You're in a Regulated Industry
Financial services, healthcare, and other regulated industries face specific AI requirements:
- EU AI Act applies if you operate in Europe
- NIST AI RMF is becoming the US standard
- Industry-specific regulations (HIPAA, SOC 2) apply to AI systems too
AI-SPM helps demonstrate compliance and maintain required controls.
You're Concerned About Shadow AI
If employees are using ChatGPT, Claude, or building unofficial AI tools, you have shadow AI. Without visibility:
- You don't know what data is being shared with AI services
- You can't enforce acceptable use policies
- You're at risk of compliance violations
AI-SPM's discovery capabilities address this directly.
You're Deploying Agents at Scale
A single agent might be manageable manually. Ten agents across five platforms? You need automation. AI-SPM provides the operational layer for managing agent security at scale.
The AI-SPM Market
AI-SPM is an emerging category, but it's growing rapidly.
According to industry analysis:
- The broader AI in cybersecurity market is projected to reach $60B+ by 2028 [MarketsandMarkets], with the LLM/GenAI security segment emerging as a distinct, high-growth category
- Over 50 companies now offer AI/LLM security capabilities
- Major acquisitions signal market consolidation: ServiceNow acquired Cuein in January 2025 to accelerate its agentic AI roadmap [ServiceNow]
- Enterprise demand is surging as agent deployments accelerate
The market is consolidating quickly. Vendors are staking claims with different approaches:
- Some focus on LLM security broadly
- Some focus on data protection for AI
- Some (like Guard0) focus specifically on agentic AI security
The AI-SPM category is coalescing around the recognition that agents are different from models, and securing them requires purpose-built capabilities.
The Cost of Not Having AI-SPM: Real Incidents
Disclaimer: The following incidents are anonymized composites based on real security assessments, public disclosures, and industry research. Specific details have been changed to protect confidentiality.
These cases illustrate what happens without proper AI security posture management.
Incident: The Shadow Agent Data Leak
Industry: Technology What Happened: An engineering team deployed a custom AI agent to help with code review. The agent had access to the codebase and could query an internal API documentation system. Unknown to security, the agent was sending code snippets to a third-party LLM API without proper data classification.
What AI-SPM Would Have Caught:
- Discovery: Shadow agent using unauthorized LLM API endpoint
- Assessment: Data flowing to external service without DLP
- Governance: Policy violation—no approval for code access
Actual Cost: 3 months of proprietary code exposed to external service. Emergency disclosure to legal. Customer notification required under contract.
Incident: The Compliance Audit Failure
Industry: Financial Services What Happened: A bank deployed AI agents across customer service, fraud detection, and internal operations. During a regulatory audit, they couldn't demonstrate which agents made which decisions, what data they accessed, or whether human oversight was in place.
What AI-SPM Would Have Caught:
- Governance: Missing audit trails for agent decisions
- Assessment: Compliance gaps flagged before audit
- Protection: Required human oversight not enforced
Actual Cost: Regulatory finding, mandatory remediation plan, $450K in consulting fees to remediate.
Incident: The Prompt Injection Breach
Industry: Healthcare What Happened: A patient-facing symptom checker agent was compromised via prompt injection embedded in a medical reference document. The agent began providing medical advice that contradicted its safety guidelines.
What AI-SPM Would Have Caught:
- Assessment: Prompt injection vulnerability in red team testing
- Protection: Content filtering on retrieved documents
- Governance: Required human review for medical advice
Actual Cost: Incident contained before patient harm, but $280K in emergency response, legal review, and agent redesign.
AI-SPM ROI: Building the Business Case
Cost-Benefit Analysis
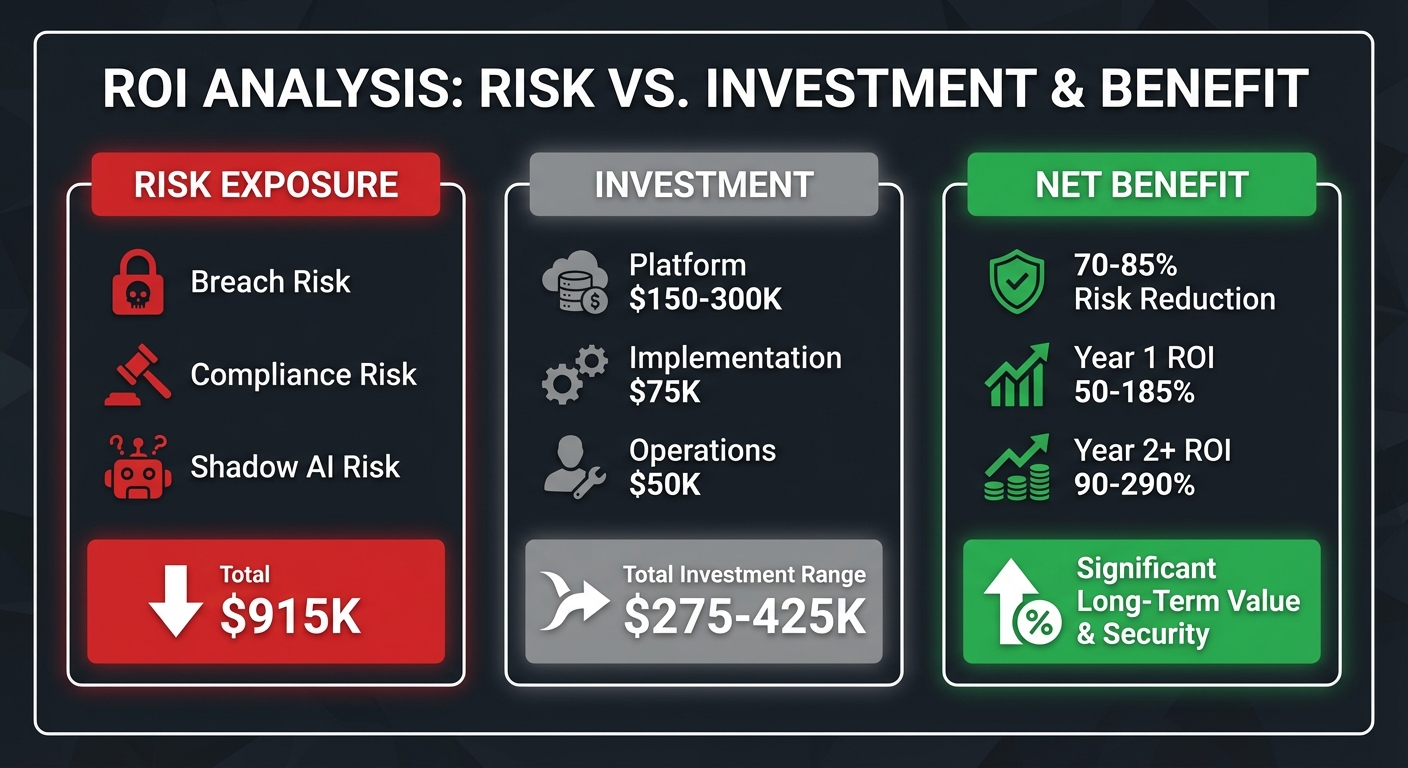
Risk Exposure (Without AI-SPM):
- Shadow AI discovery gap: 15% of agents unknown
- Average breach probability: 18% annual for unmonitored agents
- Average breach cost: $4.2M (including regulatory)*
- Compliance failure probability: 22% for first AI audit
- Average compliance remediation: $380K
*Breach cost derived from IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024
Annual Risk Exposure Calculation:
- Breach risk: 18% × $4.2M = $756K
- Compliance risk: 22% × $380K = $84K
- Shadow AI risk: 15% × $500K = $75K
- Total exposure: $915K annually
AI-SPM Investment:
- Platform cost: $150K-$300K/year
- Implementation: $75K (one-time)
- Operations: $50K/year
- Year 1 total: $275K-$425K
- Year 2+ total: $200K-$350K
Net Benefit:
- Risk reduction: 70-85%
- Risk avoided: $640K-$780K/year
- Year 1 ROI: 50-185%
- Year 2+ ROI: 90-290%
Hidden Costs Without AI-SPM
| Cost Category | Annual Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Manual discovery efforts | $80K-$150K | Staff time searching for shadow AI |
| Delayed agent deployment | $200K-$500K | Risk review bottlenecks slow production |
| Audit preparation | $50K-$100K | Manual evidence gathering |
| Incident investigation | $30K-$80K per incident | Without proper logging |
| Over-provisioned security | $100K+ | Conservative controls due to lack of visibility |
Speed-to-Value: AI-SPM Payback Period
Based on enterprise deployments:
- Week 1-2: Shadow AI discovery reveals unknown agents (immediate risk reduction)
- Week 3-4: Vulnerability assessment identifies critical gaps
- Month 2: Governance policies automated
- Month 3: Protection controls operational
- Month 4-6: Full ROI realization begins
Typical payback period: 4-8 months
Getting Started with AI-SPM
If you're ready to start an AI-SPM program, here's a practical path:
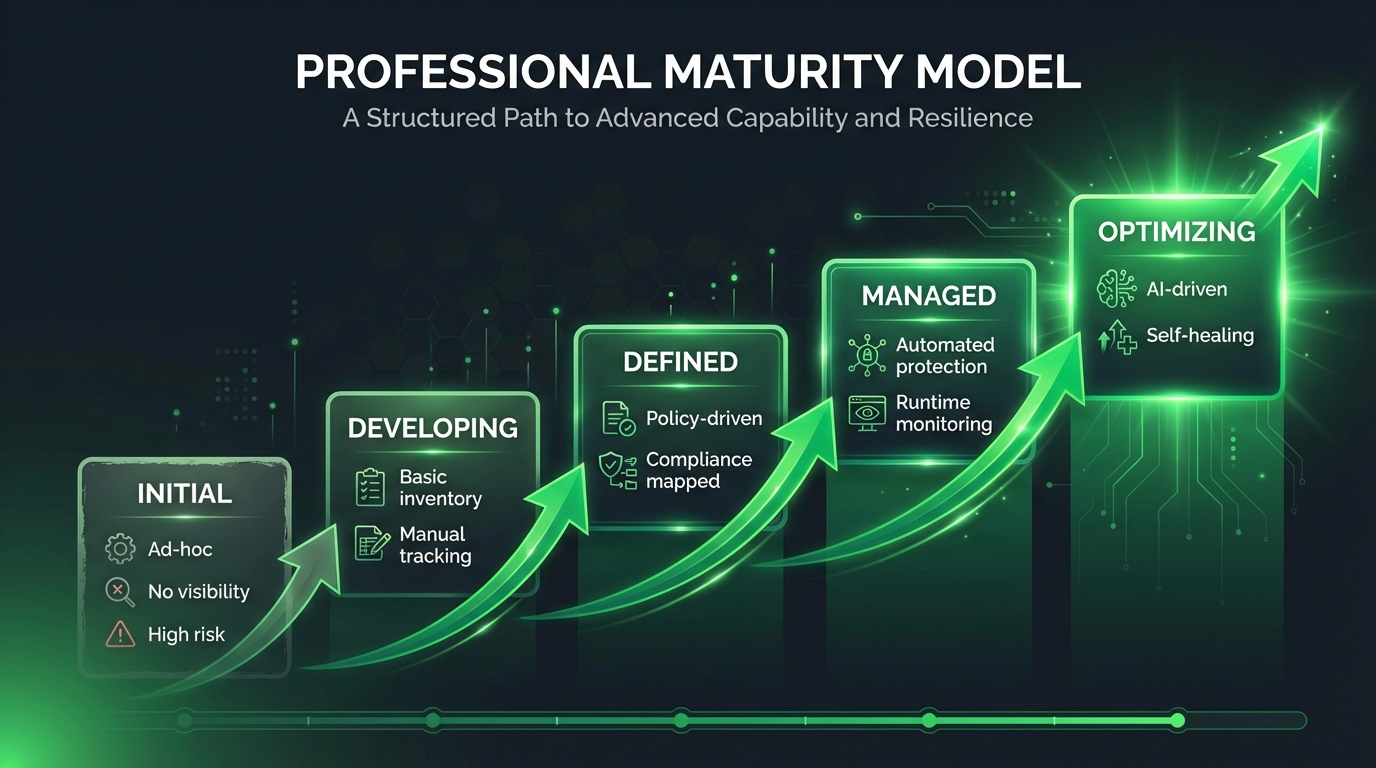
Level 1 - Initial: Ad-hoc agent usage, no visibility, no policies, high risk
Level 2 - Developing: Basic agent inventory, manual tracking, some testing
Level 3 - Defined: Policy-driven governance, policies enforced, compliance mapped
Level 4 - Managed: Automated protection, runtime monitoring, automated response
Level 5 - Optimizing: AI-driven continuous improvement, self-healing agents secure other agents
Step 1: Inventory Your Agent Estate
Before buying any tool, understand what you have:
- Survey teams about AI usage
- Check cloud bills for AI service spending
- Scan code repos for agent frameworks
- Review API gateway logs for LLM calls
Step 2: Assess Current Risks
For each agent you discover:
- What data can it access?
- What actions can it take?
- Who deployed it and why?
- Is there any monitoring in place?
Step 3: Establish Baseline Governance
Even without tooling, you can:
- Create an AI acceptable use policy
- Define an agent approval process
- Require human oversight for sensitive operations
- Mandate audit logging
Step 4: Evaluate AI-SPM Solutions
When you're ready for tooling, evaluate against:
- Discovery: Can it find agents across your platforms?
- Assessment: Does it test for AI-specific vulnerabilities?
- Governance: Does it enforce policies you define?
- Protection: Does it provide runtime security?
Step 5: Start Small, Expand
Begin with your highest-risk agents. Learn what works. Then expand coverage to more agents and platforms.
The Future of AI-SPM
AI-SPM will evolve as agents become more sophisticated:
Multi-agent orchestration: As agents work together, AI-SPM must understand agent-to-agent security
Autonomous security agents: Using AI to secure AI—agents that discover, test, and protect other agents
Real-time behavioral AI: Moving from rule-based to AI-powered anomaly detection
Regulatory convergence: As AI regulations mature, AI-SPM will become a compliance requirement
The organizations building AI-SPM capabilities today will be ready. Those that wait will scramble to retrofit security onto sprawling agent estates.
Key Takeaways
-
AI-SPM is a new category addressing gaps that CSPM, DSPM, and AppSec can't fill
-
Four pillars: Discovery, Assessment, Governance, Protection—continuously applied to AI systems
-
Agent-specific focus: AI-SPM is specifically designed for autonomous AI that reasons, plans, and acts
-
Emerging market: The category is new but growing fast as agent adoption accelerates
-
Start now: Visibility and governance can begin immediately, even without specialized tooling
References
- Gartner, "AI Adoption Survey 2024: Security and Risk Implications," Q3 2024
- MarketsandMarkets, "AI Security Market - Global Forecast to 2028," December 2024
- Forrester, "The State of AI Security, 2025"
- NIST, "AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0)"
- OWASP, "LLM Top 10 for AI Applications, 2025"
Resources
- TrustVector.dev: Evaluate the security of AI platforms before you deploy
- AIHEM: Learn agent security hands-on
See AI-SPM in Action
Guard0 is the AI-SPM platform purpose-built for agentic AI. Our four agents—Scout, Hunter, Guardian, and Sentinel—continuously discover, assess, govern, and protect your AI estate.
What you get:
- Complete visibility into all AI agents across your organization
- Automated vulnerability assessment and red teaming
- Policy enforcement and compliance mapping
- Real-time protection and incident response
Join the Beta → Get Early Access
Or book a demo to discuss your security requirements
Join our community:
- Slack Community - Connect with AI security practitioners
- WhatsApp Group - Quick updates and discussions
AI-SPM is still evolving. We'll update this article as the category matures. Last updated: January 2026.
> Get More AI Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly updates on AI-SPM, threat intelligence, and industry trends.
Get AI security insights, threat intelligence, and product updates. Unsubscribe anytime.